Making a Backup of All Foreign Keys of the Related Database in SQL Server

Hello everyone,
In this article, I will provide information on how to back up all Foreign Keys of the relevant database in SQL Server.
In SQL Server, in some cases, you may want to back up all Foreign Keys of the relevant database.
You can easily do this using the code below.
DECLARE @schema_name AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @table_name AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @constraint_name AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @constraint_object_id AS INT;
DECLARE @referenced_object_name AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @is_disabled AS BIT;
DECLARE @is_not_for_replication AS BIT;
DECLARE @is_not_trusted AS BIT;
DECLARE @delete_referential_action AS TINYINT;
DECLARE @update_referential_action AS TINYINT;
DECLARE @tsql AS NVARCHAR (4000);
DECLARE @tsqlPK AS NVARCHAR (4000);
DECLARE @tsqlFK AS NVARCHAR (4000);
DECLARE @fkCol AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @pkCol AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE @col1 AS BIT;
DECLARE @referenced_schema_name AS SYSNAME;
DECLARE FKcursor CURSOR
FOR SELECT DISTINCT OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(f.parent_object_id),
OBJECT_NAME(f.parent_object_id),
name,
OBJECT_NAME(f.referenced_object_id),
OBJECT_ID,
is_disabled,
is_not_for_replication,
is_not_trusted,
delete_referential_action,
update_referential_action,
OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(f.referenced_object_id)
FROM sys.foreign_keys f WITH (NOLOCK)
ORDER BY 1, 2;
OPEN FKcursor;
FETCH NEXT FROM FKcursor INTO @schema_name, @table_name, @constraint_name, @referenced_object_name, @constraint_object_id, @is_disabled, @is_not_for_replication,
@is_not_trusted, @delete_referential_action, @update_referential_action, @referenced_schema_name;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
BEGIN
SET @tsql = 'ALTER TABLE ' + QUOTENAME(@schema_name) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@table_name) + ' WITH CHECK ';
SET @tsqlPK = '';
SET @tsqlFK = '';
DECLARE ColumnCursor CURSOR
FOR SELECT COL_NAME(fk.parent_object_id, fkc.parent_column_id),
COL_NAME(fk.referenced_object_id, fkc.referenced_column_id)
FROM sys.foreign_keys AS fk WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN
sys.foreign_key_columns AS fkc WITH (NOLOCK)
ON fk.[object_id] = fkc.constraint_object_id
WHERE fkc.constraint_object_id = @constraint_object_id
ORDER BY fkc.constraint_column_id;
OPEN ColumnCursor;
SET @col1 = 1;
FETCH NEXT FROM ColumnCursor INTO @fkCol, @pkCol;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
IF (@col1 = 1)
BEGIN
SET @col1 = 0;
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @tsqlPK = @tsqlPK + ',';
SET @tsqlFK = @tsqlFK + ',';
END;
SET @tsqlPK = @tsqlPK + QUOTENAME(@fkCol);
SET @tsqlFK = @tsqlFK + QUOTENAME(@pkCol);
FETCH NEXT FROM ColumnCursor INTO @fkCol, @pkCol;
END;
CLOSE ColumnCursor;
DEALLOCATE ColumnCursor;
SET @tsql = @tsql + ' ADD CONSTRAINT ' + QUOTENAME('FK_' + @table_name + '_' + @referenced_object_name +
CASE
WHEN @tsqlPK = @tsqlFK THEN ''
ELSE '_' + REPLACE(REPLACE(REPLACE(@tsqlPK, ',', '_'), ']', ''), '[', '')
END
) + ' FOREIGN KEY (' + @tsqlPK + ' ) ';
SET @tsql = @tsql + ' REFERENCES ' + QUOTENAME(@referenced_schema_name) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@referenced_object_name) + ' (' + @tsqlFK + ')';
SET @tsql = @tsql + ' ON UPDATE ' + CASE @update_referential_action
WHEN 0 THEN 'NO ACTION '
WHEN 1 THEN 'CASCADE '
WHEN 2 THEN 'SET NULL ' ELSE 'SET DEFAULT '
END + ' ON DELETE ' + CASE @delete_referential_action
WHEN 0 THEN 'NO ACTION '
WHEN 1 THEN 'CASCADE '
WHEN 2 THEN 'SET NULL ' ELSE 'SET DEFAULT '
END + CASE @is_not_for_replication
WHEN 1 THEN ' NOT FOR REPLICATION ' ELSE ''
END + ';';
END;
PRINT @tsql;
FETCH NEXT FROM FKcursor INTO @schema_name, @table_name, @constraint_name, @referenced_object_name, @constraint_object_id, @is_disabled, @is_not_for_replication,
@is_not_trusted, @delete_referential_action, @update_referential_action, @referenced_schema_name;
END;
CLOSE FKcursor;
DEALLOCATE FKcursor;
When you run the above code on the relevant database, you will see a result similar to the one below.
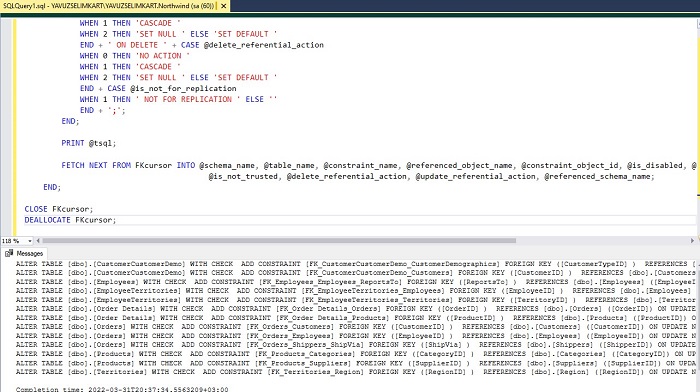
As you can see, all Foreign Key backups of the relevant database have been taken.
Good luck to everyone in business and life.


